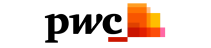An Ultimate Guide To RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is changing how businesses work by automating repetitive tasks. This helps improve efficiency and reduce mistakes. This guide explores RPA’s benefits, use cases, and importance of RPA integration to help organizations streamline operations.

For a long time, business processes have been pretty much the same - tedious, repetitive, and with very little room for creativity. However, that is all changing now with the advent of RPA technology.
Robotic process automation is automating business processes like never before and transforming the way businesses operate.
So if you're still stuck in the old ways of doing things, it's time to catch up with the times and adapt to RPA!
With the change in RPA business models like RPA-as-a-Service and new development approaches such as low-code and no-code, RPA isn’t going anywhere, at least for a decade.
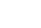
The Robotic Process Automation market is expected to grow from USD 18.18 billion in 2024 to USD 64.47 billion by 2032. This represents an annual growth rate of 17.1% during the period from 2024 to 2032.
In this guide, we'll explore what RPA is and how industries can take advantage of it.
What Is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic process automation (RPA) is an application of modern technologies like AI, ML, and NLP that are powered by business logic and structured inputs to automate mundane and repetitive business processes.
To implement RPA in business processes, software engineers build software robots that emulate human actions of interacting with digital systems like computers. These software bots can understand what is on the screen and how to navigate through the system to perform the desired task.
Assessing RPA and automation skills is crucial for companies looking to hire the right candidates. That's where assessments can be incredibly helpful in assessing technical abilities and identifying areas for improvement. By using assessments companies can feel confident that they're making the best hiring decisions possible.
How Does RPA Work?
Robotic process automation (RPA) is an excellent solution for businesses looking to automate repetitive tasks with minimal disruption. It works similarly in nature as human interaction, so you can use it on your existing infrastructure without having any issues or downtime!
With RPA, there are endless possibilities of what could be automated - from simple copy/paste activities all the way up through complex data extraction methods such as scraping web pages and downloading files off servers.
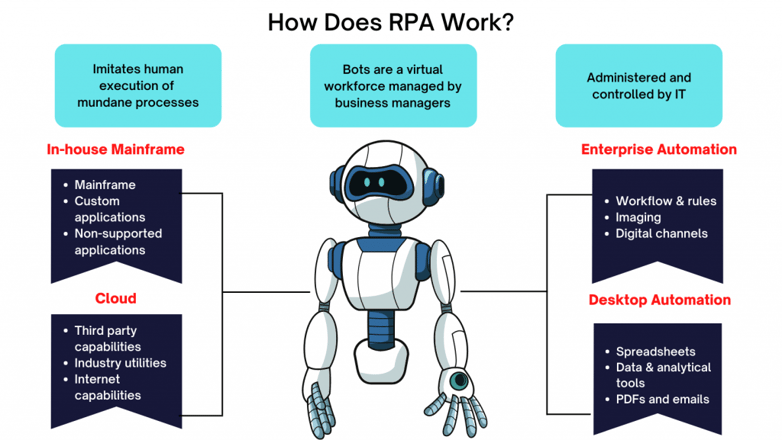
By automating these processes with Robotic Process Automation (RPA), you can create a system where bots interact and complete work assignments just like people do! This will allow minimal disruption while still leveraging existing infrastructure which makes it easy on everyone involved - especially since we know how much RPA improves efficiency.
An RPA system works by integrating with your existing technology infrastructure. RPA tools can integrate with your front-end (desktop connections) or back-end (databases and enterprise web services) to perform different tasks.
Depending on your organization’s automation needs, you can integrate RPA with either technology infrastructures or both.
- From the front-end perspective, there are several ways an RPA system can connect with your applications like Salesforce CRM, SAP, PeopleSoft, etc. RPA, at the front-end, can read and write data and record events straight from the target applications’ user interface.
- On the back-end, the RPA accesses systems and services under the governance of the process automation server to facilitate unattended automation (more on attended automation later). For example, software bots can carry out back-office tasks such as processing loan applications without requiring any human intervention when installed in the back-end systems.
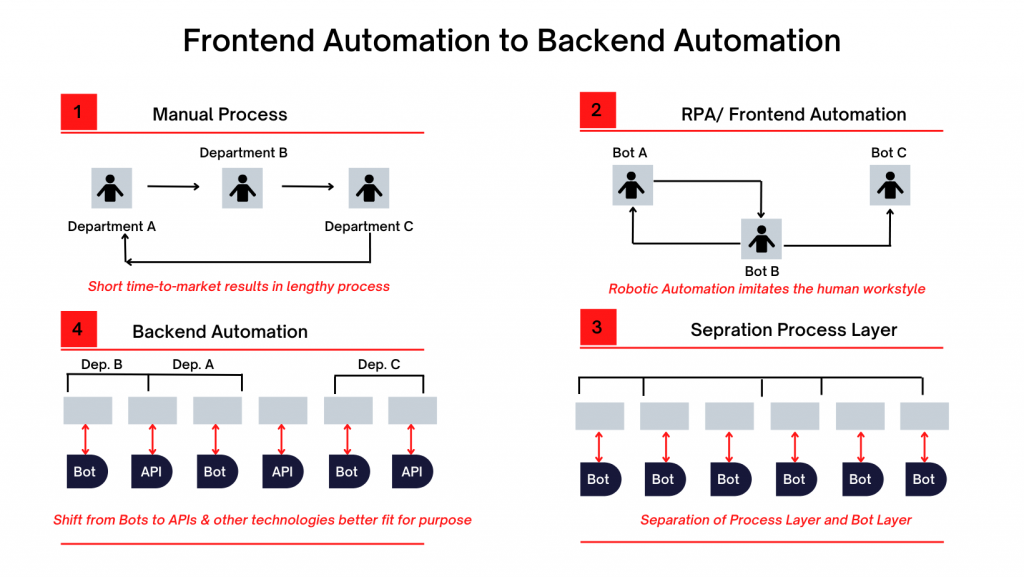
The Origin and Evolution of RPA
RPA isn’t a standalone technology; instead, it’s a combination of several technologies clubbed together as a toolkit for process automation. The term “RPA” emerged in the early 2000s, whereas its initial development took place in the 1990s.
With continuous advancement, these technologies resembled RPA very closely. Therefore, the origins of RPA relate to its three key predecessors.
- Screen Scraping is a technology that is considered a significant step toward the development of RPA. Basically, screen scraping is used to extract data from web programs and documents, which can be displayed to another application.
- Workflow automation and management tools are the nearest antecedents of RPA. These tools are used to automate processes that are repetitive in nature so that the computer program can predict the flow.
- Artificial Intelligence is the cornerstone for unattended RPA bots. Until the AI RPA integration in 2015, computer bots needed human inputs to perform tasks.
Since then, the RPA industry has been on steroids, bringing RPA among the most preferable automation technologies of modern times.
What is RPA 2.0?
RPA 2.0 is a term coined for novelty in the RPA ecosystem. After the amalgamation of RPA, AI, and Optical Character Recognition, which was named “Hyper Automation,” the automation industry is shifting towards new business models. Here are these:
- Enabling RPA as a Service: With all the prominent RPA vendors now offering cloud implementation solutions, businesses can enjoy flexible delivery methods for automation. Cloud improves scalability, and scalability brings economies of scale, which means the future of RPA is quite affordable.
- Shifting the focus on discovery tools like Process Mining: The complexity of these RPA elements makes them a niche value, but when used correctly, they can escalate the effectiveness of RPA implementation.
- Low-code/no-code (LCNC): Aimed to democratize the RPA development and deployment, LCNC capabilities are the current trend in the RPA ecosystem. Giants like Microsoft Power Automation, SAP, and UiPath are already offering some degree of LCNC capabilities with their RPA platforms.
All of the above will continue to extrapolate the RPA 2.0 trendlines. The market will also experience a gradual convergence of business process management tools and traditional RPA vendors in the future.
RPA 3.0
RPA 3.0 refers to the third wave of automation. This version combines Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), scale-based automation, and customer experience (CX). Understanding the succeeding RPA versions is important, especially given how quickly the RPA market is growing today.
RPA 2025.4
The latest version of RPA 2025.4 introduces important new features like hyper-automation, intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and better AI capabilities. This update helps businesses to:
- Speed up the use of automation across the company.
- Cut down on manual work and lower operational costs.
- Achieve greater efficiency through AI-supported decision-making.
Next, we have UiPath Autopilot with Agentic AI, which takes automation to the next level. UiPath Process Mining 2025.4 adds AI-driven predictive analytics to improve process flows before any problems arise.
UiPath Studio Pro 2025.4
UiPath Studio Pro 2025.4 also launches a new era of easier automation design. This includes features that make developing automation faster and more user-friendly. Features like Generative AI Workflow Builder allow users to create automations using simple language prompts.
Why is RPA Important Now?
According to Grand View Research, the global robotic process automation industry is expected to generate about $30,850 million in revenue by 2030. From 2025 to 2030, this industry is projected to grow at a rate of 43.9% each year.
.png?width=713&height=411&name=Screenshot%20(21).png)
The incremental growth was for the longer term, but then the pandemic happened.
The pandemic exposed the business process operations for their inefficiencies and over-reliance on manual labor. This made digital transformation leaders rethink their approach towards technologies and invest more in them. At the top of their list was RPA.
A survey by Forrester found that 48% of the organizations are increasing their spending on RPA by 5% for the post-pandemic times.
Moreover, in a study published in May 2021, Gartner found that the RPA market stood at $1.9 billion in 2020 and still was the fastest-growing software market segment.
Forrester predicts that the market of RPA software will reach $22 billion by 2022.
Looking at the industry side, the BFSI holds the largest market share while healthcare is expected to see the highest CAGR in the coming years. The industries such as IT, telecom, manufacturing, and logistics are anticipated to grow considering the demand for digital transformation and the rise in data complexity.
RPA is essential for the post-pandemic world where the employee burnout rate is skyrocketing. A recent Insider survey revealed that 61% of Americans felt “very” or “somewhat” burned out with their job. Another survey by Microsoft unveiled that 41% of the global workforce is considering quitting their current positions.
RPA implementation can help organizations:
- Free their employees up for higher-value work.
- Provide their employees with a virtual assistant.
- Increase employee inclusiveness in digital transformation.
- Retain valued employees.
Businesses can attain their automation goals depending on the type of RPA bots they implement. Let’s discuss the 3 common types of RPA bots.
Types of RPA Bots:
We’ve already discussed that RPA bots can perform predefined tasks. Depending on their implementation approach and work environment, RPA bots are generally categorized into 3 types.
1. Attended/Assisted Bots
Attended bots can be called virtual assistants that help employees with their tasks. Legacy-attended bots are limited to an employee’s desktop. In current times when RPA is getting more and more intelligent, attended bots are only suited for tasks that need to be triggered at points that are hard to detect by computer programs.
A very popular example of attended bots is in customer service operations. The employees ( customer service representatives) can trigger the bot to pull customer queries while they continue talking to them and understand their requests or grievances.
2. Unattended/Unassisted Bots
Unattended bots enable end-to-end automation that works on its own. These bots are triggered by logic in the automation process flow and have some level of decision-making ability to eliminate the need for human input. Unattended bots are the holy grail of enterprise automation strategies.
For example, the loan request at banking institutions can be taken care of by RPA bots. The software bots can simply look at the credit history and ratings of an individual to decide their eligibility.
3. Hybrid Bots
In a real business scenario, an enterprise-level automation strategy includes a hybrid automation approach where both attended and unattended RPA bots work together to increase overall efficiency and reduce human errors.
Benefits of Implementing Robotic Process Automation
Following are the most desirable benefits of RPA:
1. Reduces Cost by Increasing Productivity
In a conventional operational setup, humans are required to spend a hefty amount of time on repetitive tasks such as document scanning and verification, copying and pasting information, etc. Naturally, this increases the reliance on human labor, which is slow and costly.
The goal behind implementing RPA is to let humans work on things they excel at and let software bots take care of the rest of the tasks. RPA implementation can result in a 35% to 50% productivity increase, which triggers the economies of scale.
Also, robots are faster than human beings because they can work tirelessly 24*7. They can be active even when your entire workforce is asleep.
2. Reduces Manual Errors
Humans are prone to errors. And the chances of mistakes with mundane and repetitive tasks are as high as possible. With the right software bots implemented for the right business processes, you can sit back and relax because the software bots won’t make errors that your employees might.
Make sure that you get the implementation right. Consult an RPA software engineering team and work together to find the appropriate use cases.
3. Improves Employee Experience
Another aspect of RPA is the employee experience. For example, RPA+AI can enhance the work environment at a conventional workplace like a manufacturing facility by eliminating mundane and repetitive tasks, allowing humans to work on jobs requiring decision-making input.
4. Enhances Customer Service
Until RPA, most companies had a hard time meeting their highly varied customer demands. With RPA implemented into several business operations, you can focus more on things that matter, like customer service.
Not only this, the RPA bots can handle the screening and allocation of customer service requests so that they reach the right customer representative every time.
5. Streamline Compliance Management
RPA software’s ability to pull and aggregate data from several sources makes it the perfect tool to streamline compliance management for an organization. In addition, businesses can enhance regulatory reporting efficiency as the RPA systems can reduce the need to spend a lot of time collecting, compiling, and summarizing a huge chunk of information.
One critical aspect is the speed of an RPA system depends on the legacy infrastructure of the enterprise. Therefore, your ERP system's speed, complexity, and accuracy impact the overall automation output. Hence, it’s highly recommended to go with an experienced RPA consultancy.
Related Read: Benefits of RPA Implementation in Business
What Business Processes Can be Automated by RPA?
The use cases of RPA in business processes range from reducing payroll process errors to processing loans and customer onboarding applications. Organizations across the globe have increasingly been adopting robotic process automation (RPA) software programs to make their operations more efficient.
| BFSI and Insurance | Retail | Manufacturing & Logistics | Healthcare | Telecom | Hospitality |
| Customer onboarding
Statement processing Fraud detection Compliance management Customer query handling and communication Customer claims management Underwriting and payouts |
Invoice processing
Store inventory management Product categorization Customer support Logistics and supply chain management |
Predictive and preventive maintenance
Shipment scheduling and processing Purchase order initiation Inventory and raw material management |
Compliance management
Patient appointment scheduling Payment processing Claims management Data entry, migration, and extraction |
Compliance management
Metadata management Customer support Customer application processing Email to ticket automation |
Booking automation
Loyalty benefits processing Competitor pricing analysis Compliance management and reporting Claims processing Customer complaints handling |
Let’s discuss the business processes in several industry verticals that can be automated by RPA.
1. RPA in BFSI and Insurance
The banking and financial service industry is the market leader in RPA adoption, accounting for around one-third of the market share in global RPA revenue. Banking, finance, and insurance companies tend to deal with a lot of data, and due to this, they require a larger scale of automation.
Some of the popular RPA use cases in the BFSI and insurance domain are:
- Customer onboarding
- Statement processing
- Fraud detection
- Compliance management
- Customer query handling and communication
- Customer claims management
- Underwriting and payouts
2. RPA in Retail
The retail and consumer goods industry is expected to realize the highest growth rate in RPA adoption in the upcoming years. With online overthrowing offline, retailers have understood that higher efficiency is the key to obtaining more customers because higher efficiency results in lesser operational costs, which allows retailers to offer discounts and coupons.
Following are the common use cases of RPA in the retail sector:
- Invoice processing
- Store inventory management
- Product categorization
- Customer support
- Logistics and supply chain management
3. RPA in Manufacturing & Logistics
Core manufacturing is already largely automated, with physical robots in place. For example, the assembly line robots in the automotive industry.
Manufacturers often struggle with the cost pressure of having lower margins and the resource limitation, which restricts their focus on next-gen product innovation. RPA is implemented for these supporting manufacturing functions to make them work more efficiently.
A report by Global Lighthouse Network states that the early adopters of RPA and AI in manufacturing will realize 30-90 percent faster time to market and up to 200 percent higher factory output.
RPA can even enable intelligent upstream processes like demand planning, sourcing, and procurement. Also, for the downstream processes, RPA can infuse automation into distribution channels, warehouses, and logistics.
Following are the most promising RPA use cases for manufacturing and logistics:
- Predictive and preventive maintenance
- Shipment scheduling and processing
- Purchase order initiation
- Inventory and raw material management
4. RPA in Healthcare
Healthcare has been the most demanding industry for RPA implementation during and post-pandemic. Healthcare institutions aim to focus more on delivering value-based care and attention to patients, and in order to achieve that, they need to focus less on the back-office tasks.
Here are the more trending healthcare RPA use cases:
- Compliance management
- Patient appointment scheduling
- Payment processing
- Claims management
- Data entry, migration, and extraction
5. RPA in Telecom
With the ever-increasing demand for seamless connectivity and faster internet, the telecom sector struggles with meeting customer demands while keeping the cost lower. As a result, telecom operators deal with high overhead expenses, risk of errors, and low productivity, requiring immediate attention.
Many telecom operators have already started to automate their processes to gain a competitive advantage. Following are the top use cases of RPA in telecom:
- Compliance management
- Metadata management
- Customer support
- Customer application processing
- Email to ticket automation
6. RPA in Hospitality
We all know that travel costs are going to rise due to an increase in oil prices. Even though the increased process doesn’t demotivate people for travel, the customer expectation from the hospitality service providers will certainly increase due to higher prices. This brings a need for significant savings in operational costs.
Following are the top automation opportunities for hospitality businesses to reduce operational costs:
- Booking automation
- Loyalty benefits processing
- Competitor pricing analysis
- Compliance management and reporting
- Claims processing
- Customer complaints handling
How Do You Implement RPA at Your Company?
It is evident that RPA is necessary for operational efficiencies and competitive advantage. For every organization that is willing to invest in automation via RPA, the implementation journey remains more or less the same.
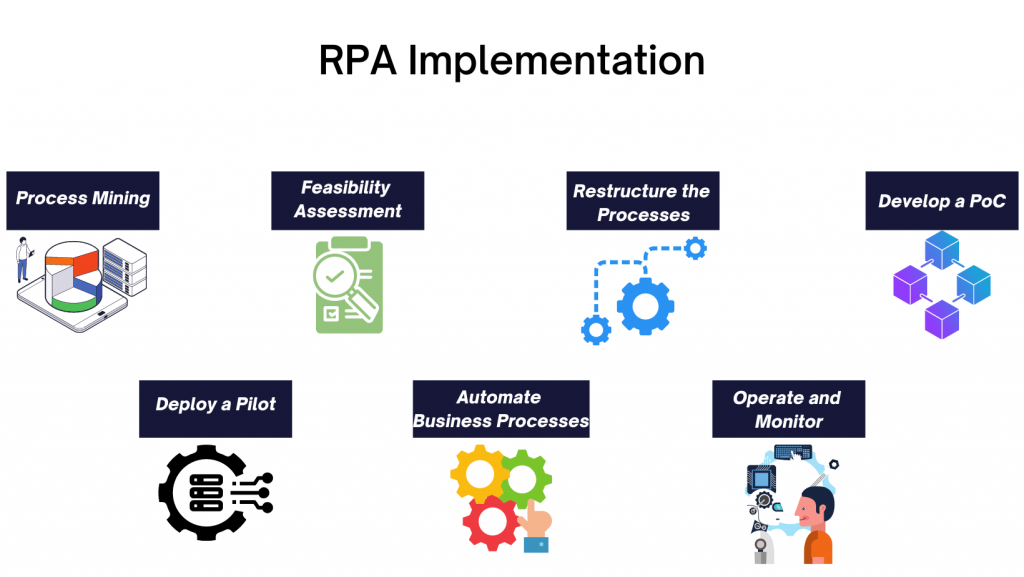
Following are the standards and steps required for a successful RPA implementation:
1. Process Mining
The automation journey in any industry starts with process mining. Because having a thought process around making the business processes efficient is the critical step for any large-scale digital transformation.
Process mining helps RPA enablers to identify business processes that can be automated. Once the process automation is up and running, you can move on to task automation.
2. Feasibility Assessment
During the feasibility assessment, the process examination and technical feasibility are carried out to evaluate to what extent a process can be automated. Most often, the actual process handler, a subject matter expert, and an RPA expert collaborate to assess the automation feasibility of a business process.
3. Readjust or Restructure the Processes
Depending on the feasibility analysis results, identify the processes that aren’t structured, standardized, recorded, and optimized for automation. You need to restructure these processes to enable automation.
4. Develop a PoC
When the processes are ready to be automated, you should first develop a proof of concept to test the practicality of RPA tools and technologies within their business environment. You should aim for automating the critical elements of business processes, not the entire process, and examine whether the automation efforts drive desired results or not.
5. Deploy a Pilot
Once you attain success in your PoC, it's time to run the pilot. During this step of RPA implementation, focus on the results. Analyze the bot vs. manual performance and determine whether you’ve invested in the correct type of RPA.
6. Automate Your Business Processes
You need to formulate an implementation plan for RPA and reorganize your teams or resources if needed. Some organizations believe they only need RPA developers for their automation journey, but that is not the case. RPA implementation requires a comprehensive team of business analysts, operating staff, subject matter experts, project managers, developers, and a solution architect.
7. Operate and Monitor
Your RPA journey doesn't end with the deployment. You need to frequently analyze the bot’s performance and ensure that they aren’t overloaded etc. Hence, it’s therefore important to partner with an RPA consultancy like Signity Solutions to ensure a successful automation journey.
How Are Businesses Leveraging RPA Solutions?
Businesses across several industry verticals are increasingly adopting RPA into their processes. Here are some of the recent RPA deployments worldwide:
AT&T’s Low-Code Automation in 2022
With the need to work from home during the pandemic, AT&T was left with unique challenges. One such case was that payments were made via phone, but the law in the US doesn’t allow businesses to access sensitive customer data such as credit card details.
AT&T implemented a low-code RPA system to curb this issue that can process payments while keeping customer-sensitive information secure. The AT&T case study showcases that solution allowed 40,000 AT&T employees to work from home effectively.
Digital Transformation Journey for the United Commercial Bank Ltd
Recently, the United Commercial Bank, one of the largest private-sector commercial banks in Bangladesh, has announced a partnership with UiPath to implement RPA to complement their overall digital transformation journey.
Skoda’s Digitalization Strategy
As part of their digitalization strategy, Skoda allowed users to utilize low-code RPA platforms to automate their daily tasks without the need for professional IT help. The low-code architect at Skoda, Jaroslav Štěpán explains that they use a hybrid model where the IT creates guidelines and the citizen developers build their automation within the limits of guidelines.
How Much Does RPA Cost?
The cost of RPA implementation depends on the number of software bots and components that make up your deployment. Generally, a single bot unit costs somewhere between $5,000 to $15,000. The cost can be broken down into several parts in which nearly 25-30% goes to licensing, and the rest is a combination of the following:
- Infrastructure setup cost.
- Hiring and training for internal subject matter experts.
- RPA vendor or consultant cost.
- Licensing cost to third-party software integration and renewals.
- Monitoring and maintenance of RPA bots.
Top 6 RPA Tools as Per Gartner
With the modern low-code/no-code approach to automation, many RPA vendors have started to offer cloud-based RPA solutions for businesses. Though these vendors claim that the no-code approach doesn’t require any technical input, we all have seen what is happening with content management systems on an enterprise level.
According to Gartner reviews and ratings, the following are the top 5 RPA tools in 2022:
1. UiPath
UiPath offers the best RPA tools and systems that are powered by AI and help enterprises automate process mining and the rest of the automation process. The platform also provides a collaboration tool where employees can request processes they want to automate.
With low-code, no-code, and full-code, UiPath can be used by any level of automation experts. Moreover, the platform offers attended, unattended, and hybrid bots to enable comprehensive process automation.
Hire UiPath Certified Developers who can effectively utilize RPA for your company to increase productivity, efficiency, and economic viability while providing unparalleled services to your partners and clients.
2. Automation Anywhere
The Automation 360 platform offered by Automation Anywhere is a cloud-native RPA solution that is largely used for legacy applications and as an RPA as a service. Automation 360 is renowned for end-to-end automation, which doesn’t require enterprises to treat back-office and front-end processes separately.
3. Blue Prism
Blue Prism is a low-code RPA platform, that allows anyone with the basic-development skills to add automation to their workflows. The platform boasts a drag-and-drop builder, which makes it easy for subject matter experts to customize tasks and infuse automation to them. Blue Prism has AI capabilities, allowing it to mimic and learn human input in business processes. You can implement Blue Prism on-premises, cloud, multi-cloud, and hybrid.
4. TruBot
Provided by Datamatics, TruBot is an RPA software designed to enable a digital workforce of attended and unattended software bots for a wide array of business processes. The software leverages the integration of cognitive applications like machine learning, artificial intelligence, and natural language processing to deliver intelligent automation.
5. OpenRPA
OpenRPA is a very simple, yet striking open-source RPA technology that is free to use and lets users automate virtually any task or process in minutes. It can automate IoT devices and is a great pick for developers.
6. Conversational RPA by AutomationEdge
Targeted to a very niche segment of business processes, AutomationEdge Conversational RPA provides employees and customers with a single-window for several operations and issues.
The software program resolves customer and employee issues and provides instant and personalized resolutions. In addition, AutomationEdge Conversational RPA offers omnichannel support through which users can enable automation by using channels of their choice like Slack, MS Teams, etc.
What Are the Factors to Consider in an RPA Software?
While there are several fantastic options available for automation, you might wonder which one I pick for my organization. Worry not; many other organizations and digital transformation leaders struggle with the same issue.
Therefore, we’re listing the factors you should consider while picking an RPA software.
- Ease of implementation. With RPA vendors offering low-code and no-code options, you need to understand your requirements. Irrespective of your choice, your RPA software shouldn’t require unnecessary efforts for implementation.
- Features. You need to consider several features like process mining, scalability, and screen slicing while selecting the best RPA software for your organization.
- Cost of ownership. While the no-code and low-code RPA software cost less, the full-code RPA software implementation costs can increase. Therefore, depending on your specific use case, you need to decide on the right RPA software.
- Vendor support. Your RPA vendor should provide you with technical and managed support if things go wrong or your developers need help.
Picking the right RPA software is not a cakewalk. As we’ve seen, the factors depend on your particular use case. Hence, it’s recommended to partner with an RPA consultancy that can guide you through your automation journey and provide technical support whenever needed.
How Can You Failsafe Your RPA Implementation Journey?
Several factors cumulate to the success of RPA implementation. Here are some high-level recommendations to failsafe your RPA journey.
- Develop a vision for the success of your RPA project. Then, list the outcomes you want to achieve with the RPA implementation.
- Put brains into process mining by bringing operation teams and RPA architects together for brainstorming.
- Ensure the reliability of your software bots by performing quality and reliability checks.
- Always start small by implementing a software bot for a couple of or a few tasks. Then, analyze their performance before scaling up.
- Partner with the right RPA consultancy to ensure higher ROI and reliability from a technical point of view.
How is RPA Different From Other Automation Solutions?
In principle, both conventional automation solutions and RPA utilize software integration to automate business processes. Still, there are several notable differences between both that make them unique.
- Technological differences: Conventional automation solutions use application programming interfaces (APIs) to bring together several systems, whereas RPA makes use of software bots to learn user actions at the interface level.
- Turnaround time: With capabilities like low-code or no-code development, RPA excels in the battle between traditional automation and RPA. While conventional automation requires complex programming and quality checks, some techno-functional developers can build automation using RPA.
- Customizability: With the subject matter, experts enabled to create bespoke automation, RPA facilitates an advanced level of customization. On the other hand, traditional automation requires changes in the existing IT infrastructure to make changes.
Why Choose Signity Solutions for RPA Journey?
Choosing the right partner for your automation journey is essential for the success of your RPA implementation. Here are the top reasons you should pick Signity Solutions as your RPA partner.
- End-to-end RPA services: We, at Signity Solutions, offer complete RPA services, including advisory, design, development, licensing, training and workshop, and support.
- Proficiency with RPA: We’ve been deploying RPA solutions for more than six years, making our implementation approach immune to errors.
- Industry expertise: So far, we’ve catered RPA solutions to BFSI, Hospitality, Healthcare, Retail, and Manufacturing.
- Top RPA experts onboard: We have the best RPA resources that can help you plan, design, and implement RPA solutions at every scale.
Future of the RPA Market
The future of RPA is bright. As several reports suggest, enterprises will continue to experiment with RPA with their business processes to achieve maximum efficiency and higher ROI.
If you’re looking for an RPA service provider to help you through your automation journey, feel free to reach us at sales@signitysolutions.com, and one of our RPA experts will get in touch with you.