RPA Use Cases in Retail and CPG Industry
Explore the transformative impact of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in the Retail and Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG) industry. Uncover innovative use cases revolutionizing operations, efficiency, and customer experiences within this dynamic sector.

Could software robots assist the physical robots in retail stores? Does RPA even offer some tangible benefits to the retail industry?
Yes, it does! And in this blog, we’ll tell you how.
These past years, the retail industry has emerged as a leader in the group of prominent and growth-oriented sectors.
But the increasing complexity and dynamic shifts have rendered the traditional methods of retail, anything but obsolete.
Retail is a low-margin but high-volume industry- meaning a subtle change in customer demand can disrupt the functioning of the entire industry. And that’s exactly what’s happening today!
With increasing competition and price-wars, sustaining a successful run in the Retail industry- be it online or offline, is a strenuous process.
The viable option to keep operations up and running effectively, however, is to offer improved customer experience & automate business processes.
That’s pretty much what this article is all about.
In this article, you’d find,
Top 7 RPA Use Cases in Retail Industry
- Sales Analytics
- Inventory Management
- Automated Stock Replenishment
- Claims and Refunds
- Customer Support Management
- Supply Chain Management
- ERP Management
Back to the topic,
Here’s an interesting proposition:
Considering the pressure, how can an organization working in the retail sector provide a better CX, and quality products at low costs?
The simple answer to the big question is Robotic Process Automation, aka RPA.
To achieve productivity, enhance employees' efficiency, and reduce operational costs, the retail industries are strategically integrating new-age disruptive automation technologies like RPA.
But before we lay bare the RPA use cases in Retail and CPG Industry, let’s shed some light on the subtle differences between these terms.
Retail and CPG: A Brief Introduction
What is CPG?
CPG, also referred to as Consumer Packaged Goods, constitute the set of commodities that is used by an average consumer on a daily basis. This includes food, clothes, healthcare, makeup, beverages, and the likes.
CPG are products that are used, and demanded by the end-consumers, and provided for by the retailers.
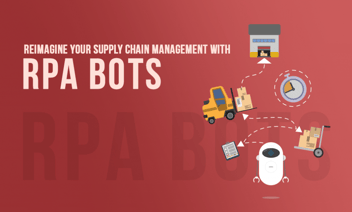
RPA Study for CPG Products:
An Accenture study marks out that over 43% of CPG executives already employ automation to cut costs and promote efficiency.
What is Retail business?
Retail includes anyone, including individuals, businesses, and enterprises, selling goods and services to the end-user. The transaction could take place either through an online store, bricks and mortar store, or cold calling.
Focusing the online aspect of retailing,
An FTI Consulting report suggests that online sales are anticipated to double by the end of 2023, accounting for over 25% of total sales in the retail sector.
The data clearly suggests that the online narrative and landscape surrounding retail is changing and investing early-on in RPA, offers a competitive edge- whilst promising accurate and reliable results in both attended and unattended processes.
With that said, let’s start with RPA use cases in Retail and CPG Industries.
Top RPA Use Cases in Retail Industry
Put simply, the role of RPA use cases in retail is to automate tasks that are repetitive in nature. Whether it’s an e-commerce website or a physical store, there is a myriad of processes in retail that are repetitive in nature and prone to errors.
RPA automates these process-driven tasks and eliminates the room for errors.
The use cases mentioned below are the most common, repetitive, yet crucial tasks to the functioning of the industries working in the retail space.
However, the list isn’t exhaustive and there are several other areas that can benefit from the right automation practices.
Read on to get to the nub of the RPA use cases in retail;
1. Sales Analytics
Conducting a comprehensive analysis of large heaps of sales data on a timely basis is essential for devising a successful marketing plan, and conducting consumer behavior analysis.

Creating and analyzing these reports manually is nothing less than a nightmare.
Use RPA bots for automating analysis and benefit from exhaustive reports outlining data, and patterns on consumer behavior, whilst pointing out their corresponding preferences.
2. Inventory Management
There are certain ‘age-old’ retail practices that are highly relevant even today! One such practice is- In-Store Planning.
Don’t be baffled over the term.
In-Store Planning, in plain English, is the practice to place products across the store in accordance with customer preferences.
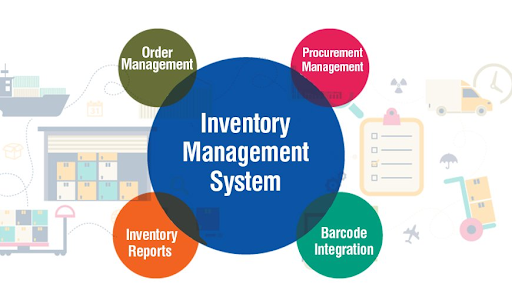
However, a human can only analyze too much information and mark decisions based on a few high-level facts. That’s not the case with Robotic Process Automation.
RPA rule-based bots study the minute details and use fine-grained data to formulate the right strategy for store-specific merchandise arrangement.
The upside?
The biggest upside is the personalized consumer experience. The customer will see what he needs, and with the right marketing practices in place, he’d be ready to spend more; ultimately, increasing your profits.
Check out this blog post to know more about the application of RPA bots in Inventory Management.
3. Automated Stock Replenishment
This point builds up from the issue we discussed in the last one (refer to point 2)- The application of RPA in Inventory Management.
Employing manual workers to access, and record inventory will inevitably result in errors. A recent survey even outlines the fact that the inventory records and stock data is inaccurate for over 63% of the time.
Your business certainly can’t afford to go wrong with inventory if you plan on playing the long game.
Employing RPA bots to record inventory will significantly bring down these errors and assist your retail business with automated stock replenishment of your primary offerings- always keeping you a step ahead of your competitors.
4. Claims and Refunds
When working in retail, know one thing- Damage is Inevitable.
You can implement steps to avoid it, but it’ll happen- either in transit, in the warehouse, or at the store itself. Though, you need not bear these expenses.

In case of damage- be it theft or physical- you need to put a claim with your suppliers and/or manufacturers.
Although, submitting proofs, and the claim process for refunds can get tedious and tiresome. Use Robotic Process Automation as the first layer to verify the submitted claims, and minimize frauds whilst reducing the claim settlement time to half.
5. Customer Support Management
The primary goal of implementing RPA for any business is to improve the overall customer experience- and this can’t be more true with retail industries.

Retailers have to pay close attention to customers’ inquiries and reactions to supplement them with better user experience. Using RPA bots as the first line of contact with your business can help you assist your customers round the clock.
Let’s take e-commerce as an example,
Living and breathing in the digital world, people are accustomed to quick services. RPA bots, when integrated with machine learning can scrutinize the previous data and automate your customer support services to provide instant assistance with both- structured, and unstructured requests.
You can even leverage RPA bot functionalities to keep your customers in the loop by sending them automated text messages intimating them regarding the different stages of their order(s).
6. Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management is essentially the last stage of any retail landscape. This stage is crucial to both- the retailers and the end customers- for it adheres to different steps that assist with product deliverability.
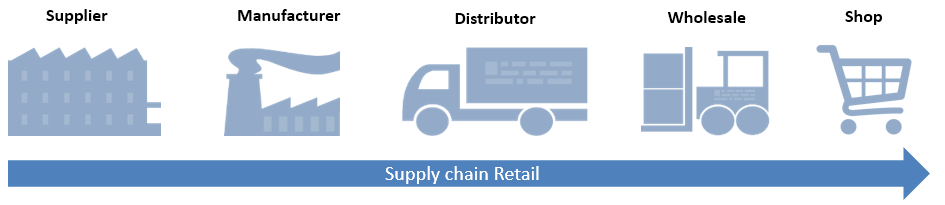
Do you know how does SCM assists with product deliverability?
The steps involved in supply chain management, include but aren’t limited to tracking shipments, inventory management, and reverse shipment (technically all the things we’ve discussed so far).
Since all these processes are repetitive and prone to clerical errors, SCM serves as a great contender for business process automation.
Robotic Process Automation can automate the communication between suppliers, customers, and distributors- which is even necessary for a successful supply chain and a streamlined workflow.
7. ERP management
Wait. What is ERP?
According to QAD, ‘ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning and refers to software and systems used to plan and manage all the core supply chain, manufacturing, services, financial and other processes of an organization.’
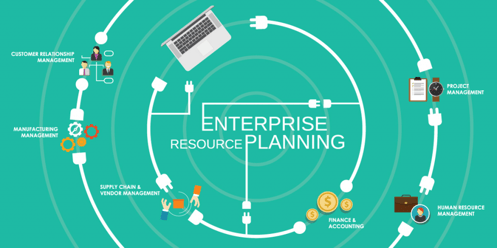
In other words, Enterprise Resource Planning includes all the essential processes like processing invoices, managing account payable, account receivable, and more.
If and when these processes are automated, your business will witness faster process time with no to minimal errors (which also adds to employee satisfaction and positivity).
The added benefit?
An RPA-powered ERP management system affects all the core areas of your retail business, i.e, adding more efficiency to Inventory management and even SCM.
Closing Thoughts
According to a PwC, the right RPA implementation has the potential to save over $2 Trillion in lost time and resources.
Do you want to be the retail business to bail out on such savings? We hope not. Signity, being a UiPath certified RPA Implementation Partner, offers end-to-end business process automation services.
If you’re new to automation or are seeking to improve upon traditional automation, our RPA services can help you with both the functional and technical aspects of business process automation.
Schedule a free RPA consultation and let our core team access your retail business to decide the best RPA implementation strategy for your business.
Thrilled about Robotic Process Automation? Check out our latest blogs to learn more about RPA and its various use cases across multiple industries.